Statistical modeling
Sara Mortara & Andrea Sánchez-Tapia
re.green | ¡liibre!
2022-07-19
about
concepts in statistical modeling
probability distributions
the linear model
1. concepts in statistical modellng
connect theory with data using statistical models
best references


best references


model & data
- data are not sacrossanct
- search for a minimal and suitable model
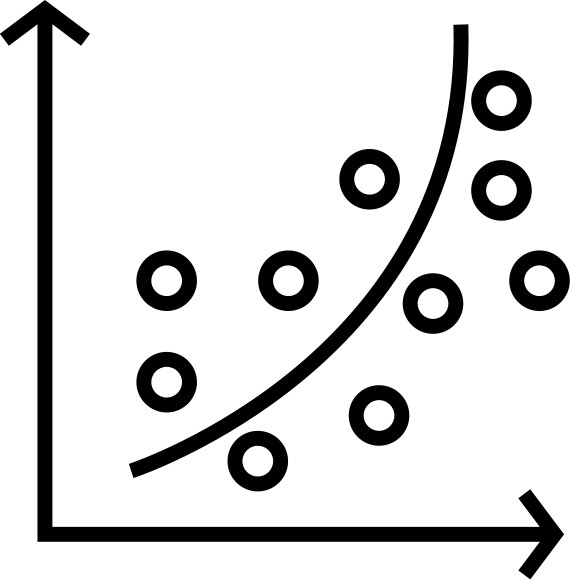
the data
- continuous or dicrete variable?
- how many replicates?
- what are the predictor variables?
- what is the pattern?
the data
- continuous or dicrete variable?
- how many replicates?
- what are the predictor variables?
- what is the pattern?
concepts
- maximum likelihood
- principle of parsimony
- Ocram's razor
maximum likelihood
given the data and the model:
what are the parameter values that make the data more plausible?
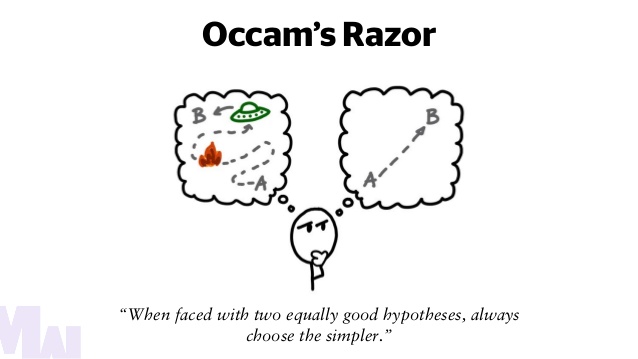
principle of parsimony
all things being equal, the simpler solution is the best
William of Occam
principle of parsimony
- models with fewer possible parameters
- linear models preferable to non-linear
- less assumptions
- minimally adequate models
- simpler explanations
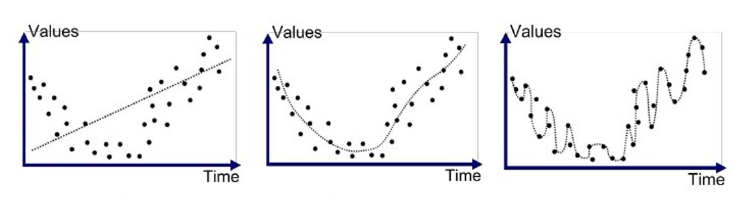
best model is just a model
- all models are wrong

- some models are better than others
- we are never sure of the correct model
- the simpler the model, the better -- but not simplistic

2. statistical distributions
statistical distributions
| distribution | type | E(X) | σ2(X) | usage | example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| normal | continuous | μ | σ2 | Symmetric curve for continuous data | size distribution |
| binomial | discrete | np | np(1−p) | Number of successes in n attempts | Presence or absence of species |
| Poisson | discrete | λ | λ | Independent rare events where λ is the rate at which the event occurs in space or time | Distribution of rare species in space |
| Log-normal | continuous | log(μ) | log(σ2) | Asymmetric curve | Species abundance distribution |
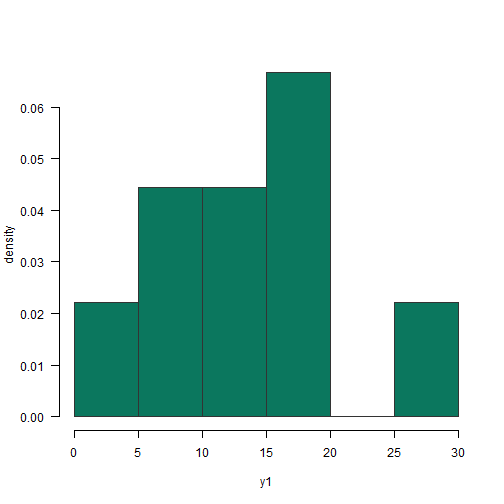
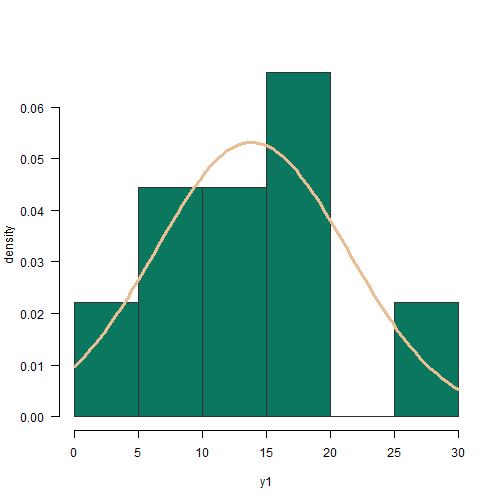
continuous distributions
df_n <- data.frame(val = rnorm(1000, mean = 0, sd = 1))df_ln <- data.frame(val = exp(rnorm(1000)))continuous distributions
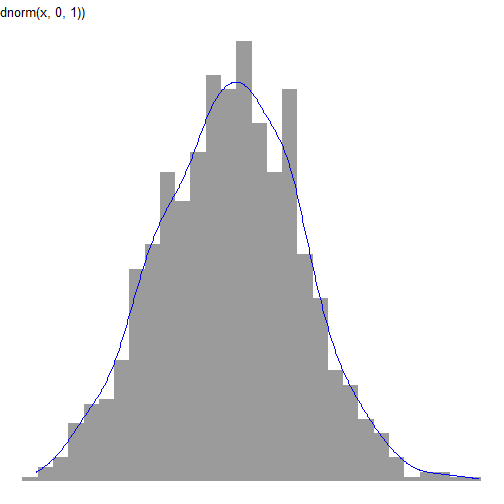
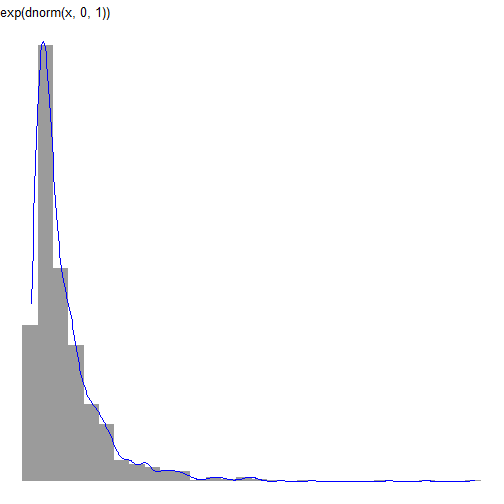
3. the linear model
mathematical model + uncertainty: Y=a+bx+ϵ
statistical model
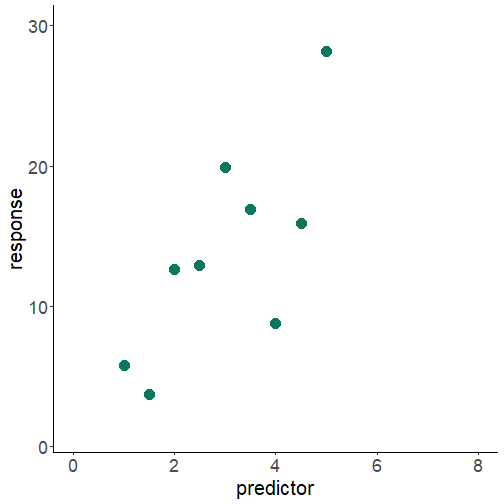
relation between variables: prediction
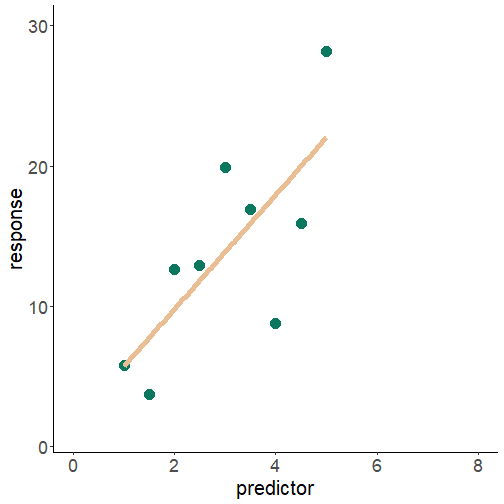
relation between variables: extrapolation
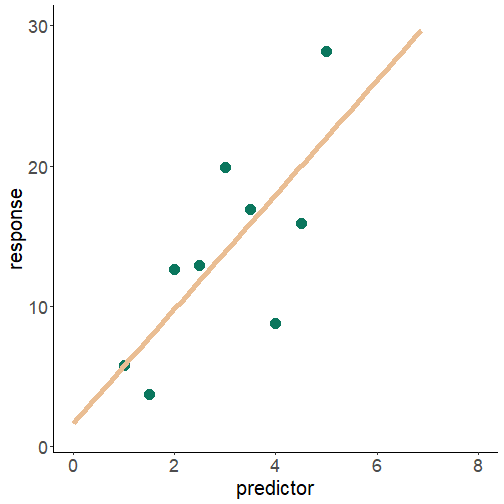
the linear model
y=a+bx
y=α+βX+ϵ
ϵ=N(0,σ)
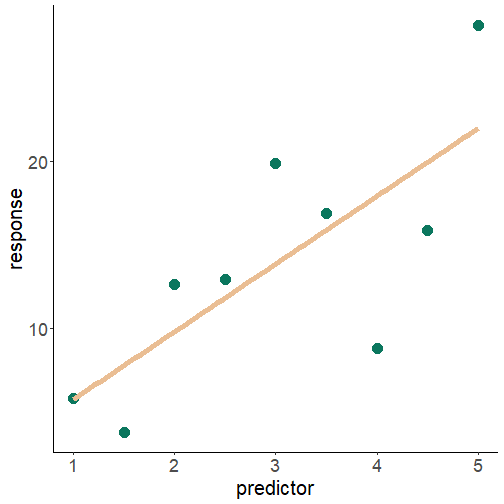
is the response variable normal?
is the response variable normal?
what is relationship between the predictor and the response variable?
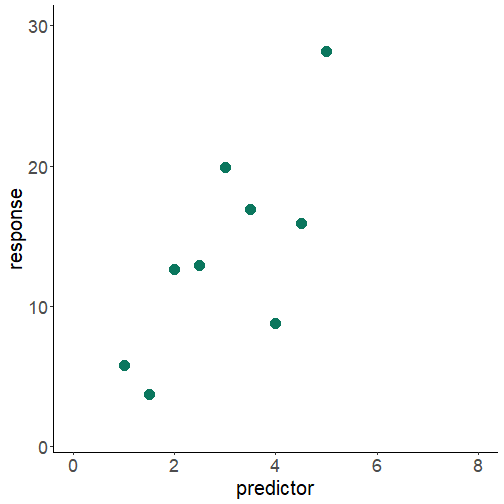
assumptions
relationship between x and y is linear
normality of residuals
homoscedasticity -- homogeneity of residuals variance
independence of residuals error terms
parameter estimation
- least squares method
- maximum likelihood
least squares method
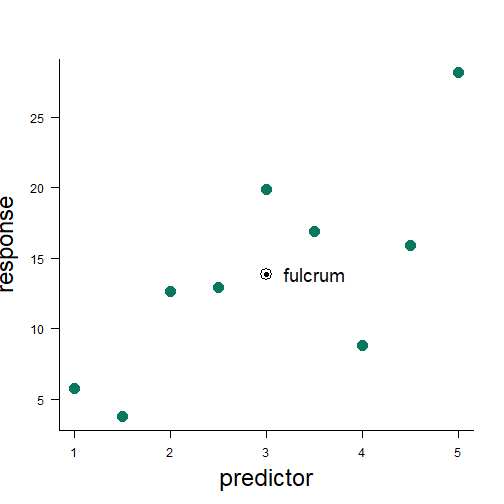
least squares method
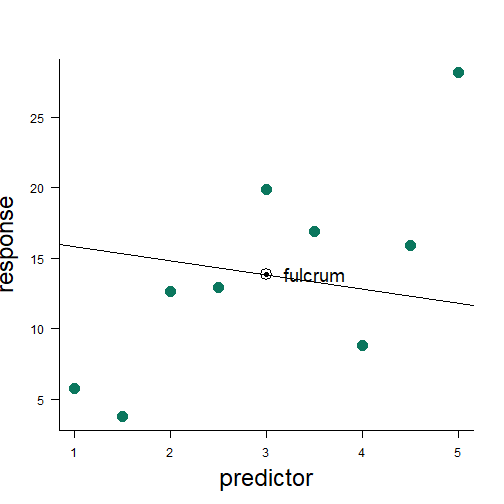
least squares method
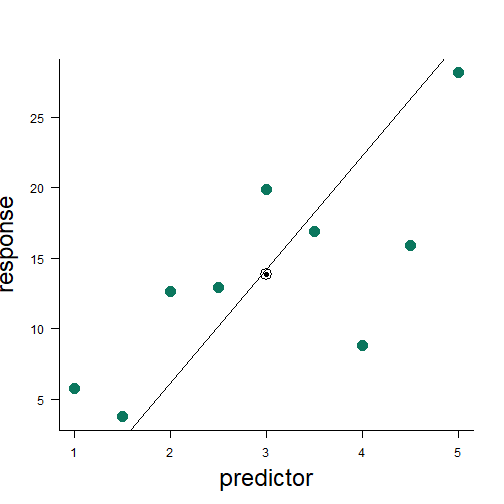
least squares method
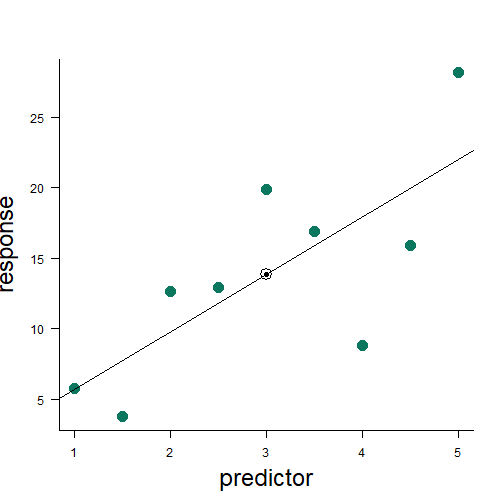
linear model in R
mod <- lm(y1 ~ x1)summary(mod)## ## Call:## lm(formula = y1 ~ x1)## ## Residuals:## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max ## -9.1424 -4.0088 0.9982 2.8714 6.1706 ## ## Coefficients:## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|) ## (Intercept) 1.632 4.520 0.361 0.7287 ## x1 4.076 1.384 2.945 0.0216 *## ---## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1## ## Residual standard error: 5.361 on 7 degrees of freedom## Multiple R-squared: 0.5534, Adjusted R-squared: 0.4895 ## F-statistic: 8.672 on 1 and 7 DF, p-value: 0.02156uncertainty in the estimate
y=1.63+4.08x+ϵ
estimation of coefficients
coef(mod)## (Intercept) x1 ## 1.632390 4.075949confidence interval
confint(mod)## 2.5 % 97.5 %## (Intercept) -9.0566136 12.321394## x1 0.8031237 7.348775linear model residue
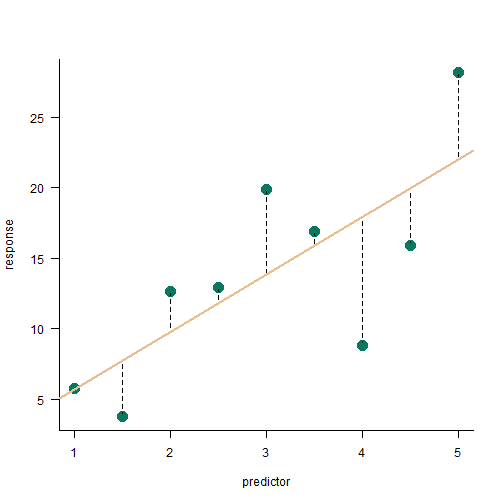
linear model variance partitioning
sum of squares from the linear model
SStotal=SSbetween+SSerror
total sum of squares
SStotal=n∑i=1(yi−¯y)2
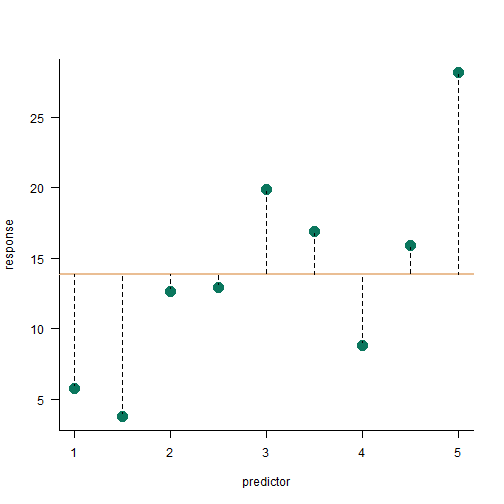
total sum of squares
SStotal=n∑i=1(yi−¯y)2
SStotal=450.35
residual sum of squares
SSerror=n∑i=1(yi−^yi)2
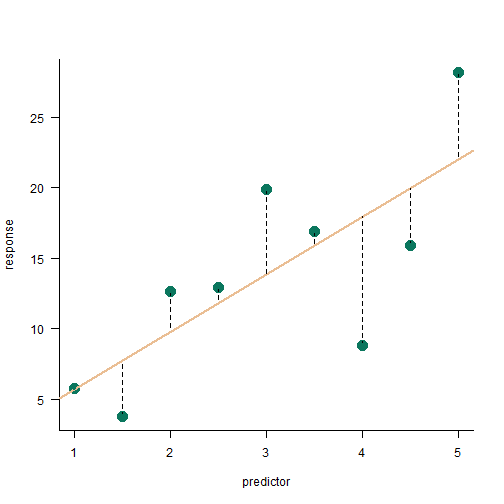
residual sum of squares
SSerror=n∑i=1(yi−^yi)2
SSerror=201.15
model sum of squares
SStotal=SSbetween+SSerror
SSbetween=SStotal−SSerror
SSbetween=450.35−201.15
SSbetween=249.2
variance partitioning
SStotal=450.35
SSbetween=249.2
SSerror=201.15
variance partitioning
anova table
anova(mod)## Analysis of Variance Table## ## Response: y1## Df Sum Sq Mean Sq F value Pr(>F) ## x1 1 249.20 249.200 8.6723 0.02156 *## Residuals 7 201.15 28.735 ## ---## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1coefficient of determination R2
R2=SSbetweenSStotal
R2=249.2450.35
R2=0.5533
coefficient of determination R2
summary(mod)## ## Call:## lm(formula = y1 ~ x1)## ## Residuals:## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max ## -9.1424 -4.0088 0.9982 2.8714 6.1706 ## ## Coefficients:## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|) ## (Intercept) 1.632 4.520 0.361 0.7287 ## x1 4.076 1.384 2.945 0.0216 *## ---## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1## ## Residual standard error: 5.361 on 7 degrees of freedom## Multiple R-squared: 0.5534, Adjusted R-squared: 0.4895 ## F-statistic: 8.672 on 1 and 7 DF, p-value: 0.02156todo
lmtutorial
git add,commit, andpushof the day